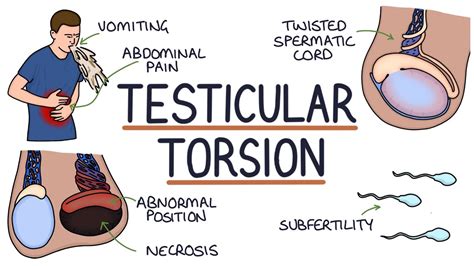
testicular torsion diagnostic test|how testicular torsion happens : exporters Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . WEB24 de jun. de 2016 · fmem is kernel module that creates device /dev/fmem, similar to /dev/mem but without limitations. This device (physical RAM) can be copied using dd or other tool. Works on 2.6 Linux kernels.
{plog:ftitle_list}
11 de mai. de 2022 · 六大DRG付费内容相关解答!. DRG付费是推进公立医院运行补偿新机制的重要手段 详解DRG分组思路,其中涉及的MDC、ADRG是什么?. 深化医保支付方式改革是党中央、国务院作出的重大战略部署,也是医疗保障制度自身发展完善、不断提高基金使用效率的必然要求 .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a.Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the .Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and an.
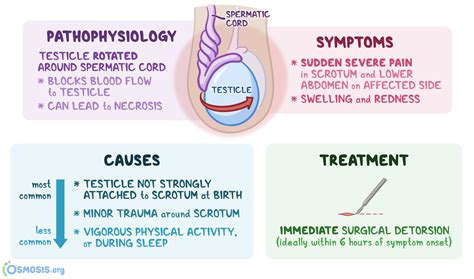
Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.
Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. A thorough history, the presence of a . However, this test cannot reliably distinguish testicular torsion from other causes of testicular pain. . Surgical exploration can confirm the diagnosis of testicular torsion. Timing is essential as torsion for greater . A history and physical examination consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consult for scrotal exploration. If history and physical examination suggest testicular torsion, immediate surgical consultation and exploration should take precedence over diagnostic tests. Usually affects young males but may affect males of .
Urine and blood tests. Samples of your urine and blood may be sent to the lab for testing, too. Ultrasound. This imaging test uses sound waves to create pictures of your testicles. The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . Medical tests that can confirm a diagnosis or help identify alternative health issues include: . (2021). https://www.nyp .
Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18. Previous testicular torsion. If you've had testicular pain that went away without treatment (intermittent torsion and detorsion), it's likely to occur again. The more frequent the bouts of pain, the higher the risk of testicular damage. Family history of testicular torsion.
Testicular torsion has an annual incidence of approximately 1 in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. 1 It is more common in children and adolescents, and delayed repair can result in the loss of . On the other hand, a negative Prehn's sign indicates exacerbation of acute pain associated with testicular torsion. Testicular torsion leads to sudden acute scrotal pain due to the spermatic cord rotating and cutting off its blood supply. This is considered a medical emergency and requires immediate diagnosis and treatment.
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, typically presenting with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. . scintigraphy using Technicium 99 pertechnate injected intravenously on an emergency basis is a valid and reliable test to diagnose testicular torsion whenever clinical and sonological findings are inconclusive [3,4]. Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . DaJusta DG, Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion in Pediatric Acute Scrotum: A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test .
American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices.A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).
testicular torsion signs on examination
Bottom line: “No discriminating features, in either history or examination conclusively differentiate the correct diagnosis when it comes to testicular torsion” (Sidler 1997) Diagnosis of testicular torsion. In patients where there is a high index of suspicion for torsion, urgent surgical consultation should not be delayed by diagnostic . Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of acute scrotal disease in children, and results in an orchiectomy rate of 42% in boys undergoing surgery fo . Testicular torsion (TT) occurs when the testis twists along the spermatic cord, compromising blood supply. 1 It is a urological emergency that requires prompt intervention. The duration of torsion is a key factor in testicular salvage rate as surgical detorsion is most successful within 6–8 hours of symptom onset. 2 Time in the emergency department is . The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion.
Testicular Torsion Diagnosis Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and give you a physical exam to check your scrotum and testicles. He might gently touch the inside of your thigh on . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity.The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis.Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency. If you think that your son has testicular torsion, he should be taken to an emergency department right away for evaluation. The symptoms of testicular torsion can seem like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his healthcare provider, or is seen in the emergency department, for a . Diagnosis Clinical presentation; Ectopic testis: Absence of a testis in the scrotum: . Testicular torsion: Acute onset of pain with a high-riding testis, swelling, very tender: Varicocele:
In this case, the doctor might recommend other tests or even surgery to remove the testicle. Blood tests for tumor markers. Some blood tests can help diagnose testicular tumors. Many testicular cancers make high levels of certain proteins called tumor markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). When these .Conditions that may mimic testicular torsion, such as torsion of a testicular appendage, epididymitis, trauma, hernia, hydrocele, varicocele and Schönlein-Henoch purpura, generally do not .How is testicular torsion diagnosed? Diagnosis entails a physical examination and a complete medical history. A prompt diagnosis is imperative because prolonged testicular torsion may cause irreversible damage to the testes. Other diagnostic tests may be done, but there is no test that diagnoses testicular torsion accurately all the time. What .
metofix vochtmeter vm125
Investigations. The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration.. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound (Fig. 4) can be used to investigate potential compromised blood flow to the testis (if available, this test has a high sensitivity (89%) and . Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates around the spermatic cord, which provides blood to the scrotum (a bag of skin that contains the testicles). Testicular torsion typically affects adolescents, although it can occur at all ages, including newborns and older adults. . Additional diagnostic methods include urine tests to exclude .If history and physical exam suggest testicular torsion, immediate surgical consultation and exploration should take precedence over diagnostic tests. Intraoperative photograph showing extravaginal torsion of the spermatic cord and the necrotic testis in a newborn with discoloration of the right testicle at birth
Intermittent testicular torsion (ITT) is a syndrome associated with recurrent scrotal pain secondary to torsion of the spermatic cord with spontaneous detorsion. 1, 2 While the long-term effects of ITT are not well described, it is thought that these episodes can be antecedent to acute torsion with a risk of testicular loss. Reports indicate that up to 50% of . Testicular torsion, also termed torsion of the spermatic cord, is a relatively common and potentially devastating acute condition resulting from obstruction of the arterial blood supply to the testis. [] Fortunately, this entity is relatively well known, and it usually occurs with enough discomfort to lead to its diagnosis and subsequent testicular salvage.
mettler toledo vochtmeter
WEBRio de Janeiro, RJ. Página oficial. sepm.rj.gov.br. A Polícia Militar do Estado do Rio de Janeiro ( PMERJ) tem, por função primordial, o policiamento ostensivo e a preservação .
testicular torsion diagnostic test|how testicular torsion happens